Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
How are packets transported at the network layer?
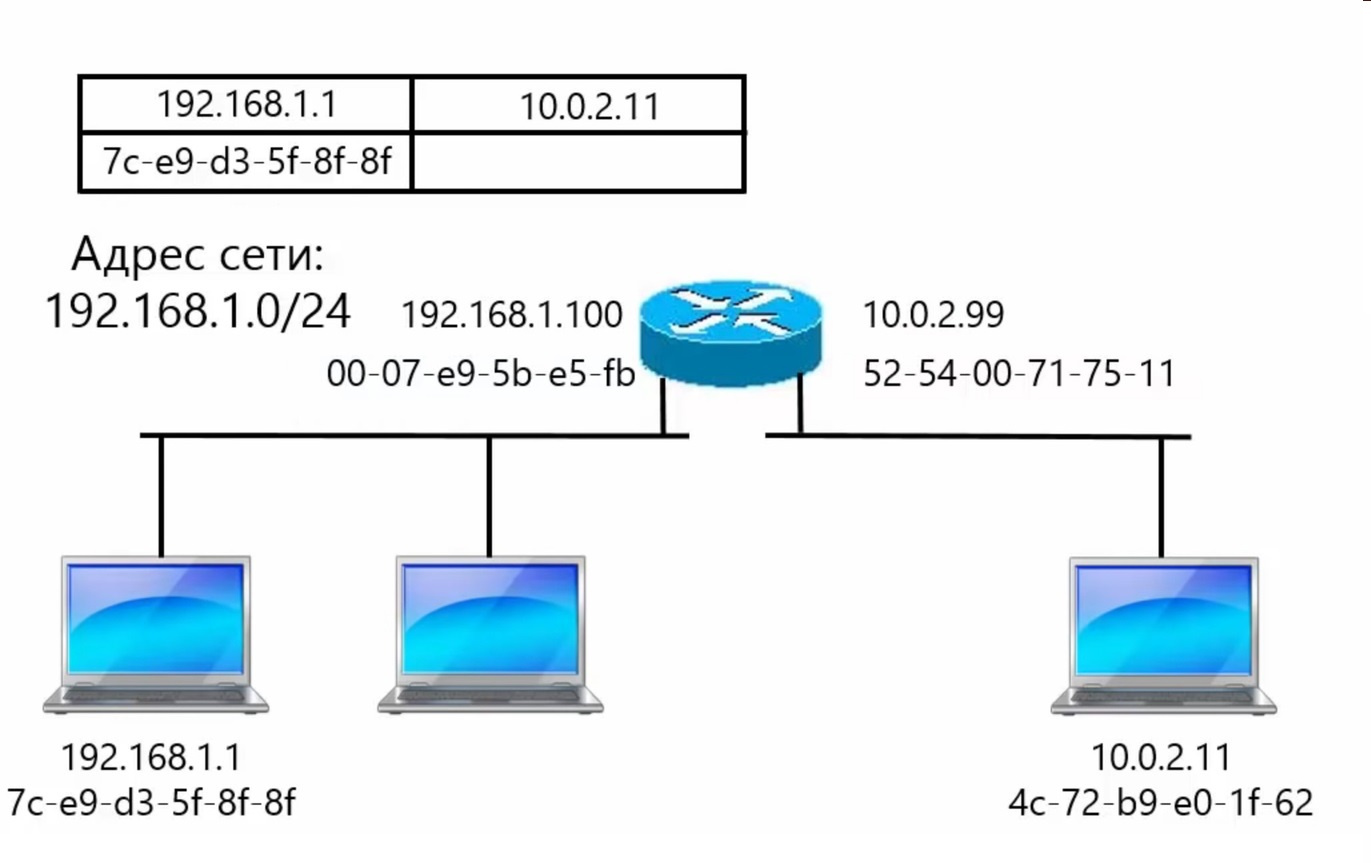
Considering the network (in the picture) at the network layer of the TCP/IP model
The picture shows that the router has two different ip-addresses (as well as MAC) for different subnets. Why is it so? Why can't you use the same IP address and MAC?
Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
Because the IP address must belong to the network in which the computer is located. The router is on two networks at once, so it needs an address on each network.
MAC addresses are usually not set manually, but take those addresses that are programmed into network cards. Therefore they are different. Purely theoretically, in this case, you can set the same MAC addresses and nothing will break, because the cards look at different networks. But this is an extra gesture. It's better to use the default address and not worry.
Because the gateway address must be from the same network as the workstations. Since your machines are on different networks, you need two addresses, one per network.
Here it is not necessary at all. The MAC address on the router interfaces can be the same, it only matters within the same network. Moreover, in real situations, when you have one physical port on your router, and networks are separated by VLANs, most often the poppy will be the same for each logical interface within one physical one.
Didn't find what you were looking for?
Ask your questionAsk a Question
731 491 924 answers to any question