Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
Locking pages in co-authoring
Good day.
There is such a database structure.
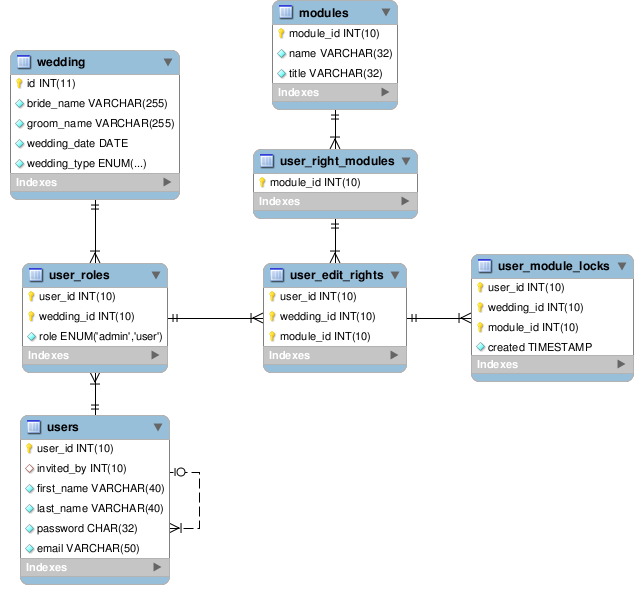
Short description:
users — table of users.
user_roles - the user's role in a particular wedding, the user can participate in editing
several weddings.
wedding - table of weddings.
user_edit_rights - User rights in a particular wedding to edit a particular module.
user_module_locks - User locks of a specific module
user_right_modules - list of modules that can be edited.
modules - a list of all modules on the site.
The task is to block individual pages for joint editing,
that is, so that only one user can edit the page.
I decided to do this:
1. After the user enters the page, the following request is executed.
The result of its execution looks something like this:
SELECT
users.user_id,
modules.module_id,
IF(user_edit_rights.user_id = users.user_id, 1, 0) AS user_can_edit_module,
my.module_id AS user_lock_module_id,
IF(other.user_id != users.user_id,1,0) AS another_user_lock_module
FROM users
INNER JOIN user_roles ON users.user_id = user_roles.user_id
INNER JOIN wedding ON wedding.id = user_roles.wedding_id
LEFT JOIN modules ON 1
LEFT JOIN user_edit_rights ON user_edit_rights.user_id = users.user_id AND user_edit_rights.wedding_id = wedding.id AND user_edit_rights.module_id = modules.module_id
LEFT JOIN user_module_locks AS my ON my.wedding_id = wedding.id AND my.user_id = users.user_id
LEFT JOIN user_module_locks AS other ON other.wedding_id = wedding.id AND other.module_id = modules.module_id
WHERE users.user_id = 3285
AND wedding.id = 72
AND modules.name = 'gifts'
| user_id | module_id | user_can_edit_module | user_lock_module_id | another_user_lock_module |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3285 | ten | 0 | 2 | 0 |
Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
Yes, all this is normal, and a bunch of joins, and keys, when a relational base is used for object models. Make materialization, create convenient conditions for popular samples due to data redundancy, or use key-value storage.
Can a user edit a specific wedding, while not being its customer, nor being an admin or manager? If yes, then the following questions:
- who gives permission for the right to edit
- can permissions be removed from the abstraction of the database module (while it is possible to leave abstractions in the interface)
More questions
- do user roles change dynamically? Is there a lot of confidence that it is needed in this form? If yes, then why can't you add a role as a variant of the whole value of the field, and just save its description - why a separate table for them?
- blocking - only for individual weddings? If so, why can't you create a single table with privileges?
In general, you are right - your hands are itching to optimize ... and greatly optimize. True, there are slight doubts that it is possible to advise something very useful on the basis of the information presented. The advice will be much more objective if you look at the ToR.
Didn't find what you were looking for?
Ask your questionAsk a Question
731 491 924 answers to any question