Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
How to collect network download statistics? How to block access to resources and ensure security?
It would be appropriate to do the various questions separately, but I want to paint a holistic picture for myself first. It won't work separately. Please, the opinion of a person who reads the question in full is important to me, otherwise you can not write anything, do not waste either my or your time.
Initial:
I work in a service company
Windows domain network, DC based on Windows Server 2012 (domain level so far 2008R2)
As a proxy ESERV4
Mikrotik software (hereinafter MK) RB2011UiAS-2HnD-IN - gateway, ether1-ether5 is busy on it
Key most used applications requiring WAN connection: mail, browser, skype, ammyy admin, teamviewer, rdp.
The key most used applications that require a connection to the LAN: rdp, 1c, file shares (DFS on DC), telephony (software asterisk + software softphones for workplaces + their own VOIP gateways)
I briefly compiled a network diagram, see the figure below.
In general, the question: I am interested in the issue of performance analysis in the context of the network and network security. In the background, performance management through constraints. Further details.
1) To analyze the workload, I need to check what is going through the mikrotik (WAN) gateway for the selected period of time, that is, information must be collected constantly. I already tried to ask a similar question here How to analyze the volume of traffic passing through the WAN?Since then I have tried more. For starters, since then I have passed MTCNA, MTCRE certificates so I can swear by words like OSPF and BGP.
I need information of the following nature, based on the order in which the reports are viewed:
- is there a load on the WAN in accordance with the bandwidth provided by the provider (in my case, always in most cases during working hours at the peak value)
- at what point in time did peaks occur in working hours
- who created this load (ip, dns computer name) at the time of peaks
- where did this person go, what resources did he use, what created the load at this peak time and how much traffic in the context of a particular case from the general schedule for the day
IMPORTANT: For all these points, below I will describe the software that I tried. I came across software in which you can see that yes, this person, looking at the general schedule and the schedule of this person, created a load, at the moment, with such a volume of traffic. However, there is useless software where it is indicated separately that a person went here and here and here is his traffic volume, but it is not tied to time, and even sometimes the software shows in the format not Mbps, but in general MB. In other words, you cannot compare time graphs and traffic graphs, they live separately, for example, ntopng software.
IMPORTANT: The software is preferably not expensive for these purposes, since the authorities will not let you buy everything. Opensource would be great.
1.1) the channel bandwidth was increased to 15Mbps, but this did not solve the problem of the slow speed of applications requiring an Internet connection 1.2) To try to collect information through netflow and analyze it, except for ntop
(still the same 460304) I tried the following programs:
1.2.1) ntopng - does not show the necessary information
1.2.2) netflow analyzer - The program does not work correctly, the interface accessibility regularly disappears. There is no way to correctly bind mikrotik parameters, in particular, interface names are not displayed correctly, which makes it difficult to understand what I’m looking at at all, for example, Infef82 it seems I don’t remember exactly
1.2.3) the dude - has a link to the microtic architecture, not all mikrotiks support the dude, in particular mine does
not and use this crap
1.2.5) Paessler PRTG is expensive, the authorities won’t buy it, so I didn’t even consider it
IMPORTANT: In turn, in mikrotik courses, I managed to get bored with everyone already with a question on netflow to both the teacher and neighboring students, despite the fact that some students are from provider companies. Nobody stupidly knows how to handle netflow + mikrotik. The question, of course, is not in setting up on the side on mikrotik, there are generally 2 keys to press, but the question is to assemble it and in a normal form could be analyzed. In the end, the teacher said that this question was purely optional and was not considered on the course, and he himself dealt with netflow mikrotik once or twice, according to him.
2) Based on point 1 (despite the fact that I have not solved it), there are several problems:
- it is not possible to trace who specifically created the load if it comes with RDP. + - 30 users work on RDP, respectively IP will not tell me anything in the context of the user
- In the future, it is not possible to block access to specific resources on mikrotik. Let me remind you that I have Mikrotik certificates. The teacher, in turn, said that it is generally better not to use a proxy on mikrotik, an atavism, it is better to use a separate proxy server. In turn, before the courses, I tried to use a proxy on the MK. Put only the enable checkbox in the proxy and the processor on the MK on an ongoing basis at least 90%. In addition, the MK proxy does not know how to work with https traffic. So the note was taught earlier by me and checked for the stability of the statement.
2.1) I’ll say right away I’m not familiar with the proxy, only a theory, like Mikrotik at the time of my first acquaintance with Mikrotik 2 years ago. I set the ESERV4 proxy. Tried to persuade the administration to refuse in favor of squid or other software. I can not refuse it because of the elementary imposition of it by the authorities. Unfortunately, the administration does not allow me to enter squid, arguing WellAnoZheKaktaWorkedBefore, despite the fact that former colleagues, like me, did not master this crap.
2.2) ESERV4 works as a proxy successfully, but the problem is to distribute this proxy to everyone. Given that there is a DC distributed to everyone through the GPO and tightly tied so that it could not be changed. However, this proxy is distributed only on IE. Well, for example, ammyy admin picks up his settings, but thunderbird, firefox do not. The most resource-intensive in the context of the network is of course the browser. How to bind a hard proxy to such applications? And if someone portable launches past me? And if other applications appear?
2.3) Here I have a gap in knowledge and, accordingly, doubts whether it is possible to bind a proxy to a computer as a whole and not to applications? That is, for example, at least ammyy admin does not have the same load compared to the browser, but I want to see it through a proxy. In this application, it's not a problem to put "no proxy". Hence the question is it possible to use the computer as a proxy client in general, for example socks? Or are socks just separate applications that do not know how to work using the http protocol, like skype? That is, why should applications on the computer turn to the proxy and not the computer as a whole act as a proxy client? A crazy question, but that's why I say that I have a gap in knowledge.
3) I want to use a proxy as an addition to point 1. That is, in the proxy, you can view everything that I need in point 1, for example, using the proxyinspector software for eserv. On the proxy, respectively, I will already block specific resources in order to weed out obviously known unnecessary sites for use by employees. Perhaps in addition I will use queue on mikrotik. The problem is in paragraph 2, questions.
4) Looking at the diagram that I attached, I have a question, should the central switch (cabinet 1), taking into account the fact that there are 5.7 servers in the cabinet, be replaced with a managed one? Here, despite the certificates, I still have enough spaces. I can’t understand and write for myself, and accordingly argue in detail with the management, I have suspicions that glitches and slow speed of applications in LAN with local resources occur, among other things, due to the fact that individual switches are not controllable, which means communication via ARP is going on much more often than necessary? The logic is as follows: if the switch is not managed and from a cheap segment, then at least at the time the connection is established and the packet is assigned to a specific port for the first time, it will poll all its ports and then send the packet. In addition, what is the routing table in these switches, how long does she live there, to what extent, how often is it cleaned compared to the same, for example, MK? Accordingly, how often, taking into account all these operations, does the switch perform all this and does it have a load, does it have a queue?
5) there are also access points on the diagram, using which clients connect to our network. With my scheme, how can they be thrown separately into another network in order to assign appropriate operation rules to them, but at the same time they will communicate with the main network? At the moment, everything is in one heap on the network 192.168.0.0/24. How to properly throw users into a separate subnet? For example, I considered the option of managed switches by cabinets, then VLAN to separate wfi traffic of users from the rest, and on the MK, respectively, combine these networks. In turn, authorize on the same DHCP on the DC (DHCP is one on the network at the moment) but, accordingly, make a bracket for them with a different mesh 192.168.1.0/24. Accordingly, separately wifi users can generally limit the total traffic above which they will not jump without bothering.
That is, the question is that I want to throw wifi users into a separate network in order to:
- they do not clog the dhcp bracket in the network
192.168
.
/24 only individual hosts from 192.168.0.0/24 and nothing else. I myself don’t know yet how to implement it, maybe I’m already talking nonsense from fatigue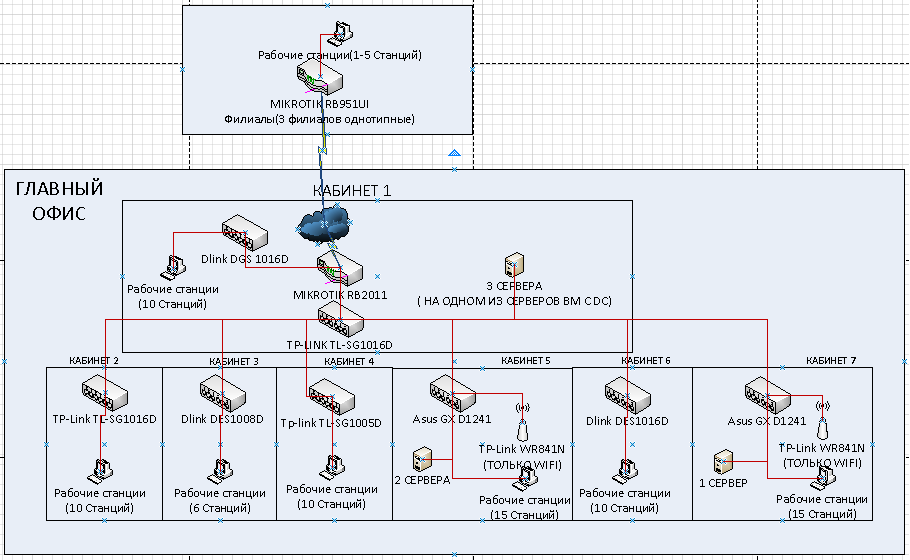
Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
You seem to have the wrong approach, monitoring of such a level is simply not needed to resolve this situation.
the channel bandwidth was increased to 15Mbps, but this did not solve the problem of the slow speed of applications requiring an Internet connectionYou need to understand that different applications have different requirements. And it is far from always that the bandwidth of the channel is needed.
A person with certificates, who can "swear" about BGP and OSPF, could not deal with the dock using nfdump ... Actually, comments are superfluous.
nfdump can show everything - and where the traffic comes from, and where, and in how many streams, and how much per unit of time.
Didn't find what you were looking for?
Ask your questionAsk a Question
731 491 924 answers to any question