Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
Why do you need a root certificate?
Second attempt ;)
Actually, I understand that the root certificate signs all the others and allows you to make sure that the site certificate is real.
But.
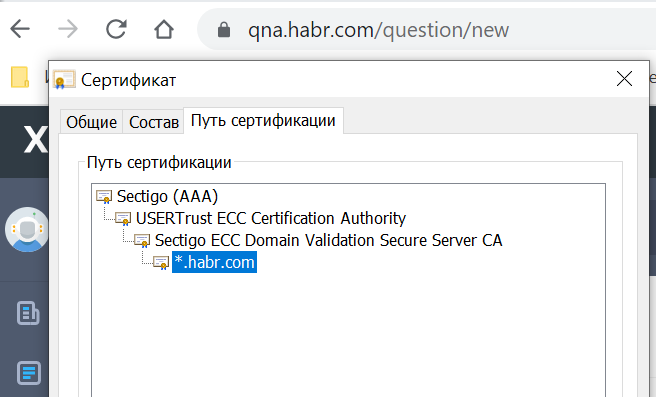
Sites usually already give the entire chain of certificates, including the root.
Why is it usually added to the system? Oo
Well, his site gives away!
Or are the root certificate on the site and in the system two different entities?
Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
Well, just imagine: the fraudster Vasya issued a root self-signed certificate. And then he signed the chain to the phishing site mmoney.com
User Petya went to the site, received the entire chain of certificates, including the root certificate; the chain is, of course, valid. And he entered his credit card details, being sure that he was dealing with a normal site.
To prevent this from happening, not only the certificate chain must be valid, but the root certificate (from which the chain actually begins) must be recognized as reliable. This is why trusted certificates are added to the operating system (and the user can add a new root certificate himself if he considers it trustworthy)
It's a matter of trust. Certificates can be signed by other certificates, this guarantees the integrity of the chain, but in the end all this must be certified by a party that you (the browser) unconditionally trusts.
If a site sends you a root certificate, how can you trust it?
Propagating these root trust points is an important part of building the entire PKI (Public key infrastructure) system, and is not a cryptographic problem, but a socio-technical one.
Didn't find what you were looking for?
Ask your questionAsk a Question
731 491 924 answers to any question