Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
Typescript generic function. How to use with other types?
/**
Example array
*/
arr = [
{
name: 'John',
author: 'Bender',
year: 2003,
text: [
'Lorem ipsum',
'Lorem ipsum',
'Lorem ipsum'
]
}
]
/**
Example generic function
This function should sort array
*/
function sortArray<T extends [], K extends keyof T> (originArr: T, propertyName: K, cb: (a: T) => T): T {
let arr: T = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(originArr)); //deep copy array
let resultSort: T = arr;
resultSort = arr.sort((a: K, b: K) => {
let nameA = a[propertyName].toLowerCase(), nameB = b[propertyName].toLowerCase();
if (nameA < nameB)
return -1;
if (nameA > nameB)
return 1;
return 0;
});
return cb(resultSort);
}let nameA = a[propertyName].toLowerCase(), nameB = b[propertyName].toLowerCase();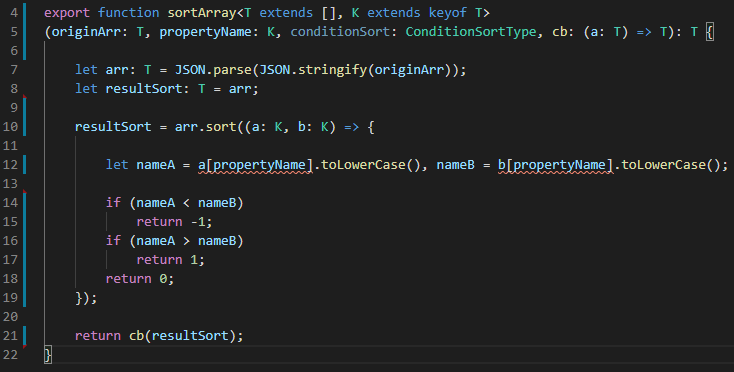
Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
No, there are a lot of problems here.
T extends [], K extends keyof T- Kthere is something derived from number, because the keys (keyof) of the array ([]) are only numbers.
let resultSort: T = arr;- meaningless, since it arr.sortchanges the original array anyway.
a[propertyName].toLowerCase()- will fall if propertyNameit is year, because Number does not have a toLowerCase.
...
As a result, the function should look something like this:
function sortArray<T extends {[key: string]: unknown}, K extends keyof T> (originArr: T[], propertyName: K, cb: (a: T[]) => T[]): T[] {
let arr: T[] = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(originArr)); //deep copy array
arr.sort((a, b) => {
let nameA = String(a[propertyName]).toLowerCase(),
nameB = String(b[propertyName]).toLowerCase();
if (nameA < nameB)
return -1;
if (nameA > nameB)
return 1;
return 0;
});
return cb(arr);
}String, but then instead unknownyou need to specify the specific types with which you are supposed to work, and take them into account in the sorting function itself.
Didn't find what you were looking for?
Ask your questionAsk a Question
731 491 924 answers to any question