Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
I don't understand what is the error in the code, how can I fix it?
I am writing a program that calculates the equation for this formula (-2 * c - d + 53 - e) / (a / 4 - 1 + f) but when I check for si, my answer is completely different. Here is my code
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstdlib>
int main()
{
signed char a, c, d,f,e, res_c, res_asm;
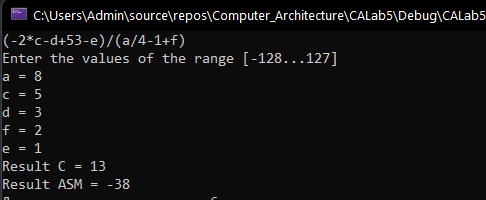
printf("(-2*c-d+53-e)/(a/4-1+f)\n");
printf("Enter the values of the range [-128...127]\n");
printf("a = "); scanf_s("%d", &a);
printf("c = "); scanf_s("%d", &c);
printf("d = "); scanf_s("%d", &d);
printf("f = "); scanf_s("%d", &f);
printf("e = "); scanf_s("%d", &e);
res_c = (-2 * c - d + 53 - e) / (a / 4 - 1 + f);
printf("Result C = %d\n", res_c);
__asm {
mov al, c;
mov cl, 2;
imul cl;
mov cl, 1;
idiv cl;
mov bl, al;
mov al, d;
sub al, 53;
add al, e;
add bl, al;
mov al, a;
cbw;
mov cl, 4;
idiv cl;
mov dl, al;
add al, 1;
sub al, f;
xchg al, bl;
cbw;
idiv bl;
mov res_asm, al;
}
printf("Result ASM = %d\n", res_asm);
system("Pause");
return 0;
}
Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
Well, let's take a look at the beginning:
mov al, c;
mov cl, 2;
imul cl;
mov cl, 1;
idiv cl;
// делим 2*c на 1? зачем?
mov bl, al;
mov al, d;
sub al, 53;
add al, e;
// d-53+e? почему сложение и вычитание везде перепутано?
add bl, al;
// bl = 2*c+d-53+e
mov al, a;
cbw;
mov cl, 4;
idiv cl;
mov dl, al;
add al, 1;
sub al, f;
// al = a/4+1-f ??
xchg al, bl;
cbw;
idiv bl;
// al = (2*c+d-53+e) / (a/4+1-f)
mov res_asm, al;scanf_s("%d", &a);it is not possible. 4 bytes will be written to a one-byte variable. MS VS, as I understand it, cannot read a number into a variable of type char normally, so you have to tinker with it somehow:int ai, ci, di, fi, ei;
...
printf("a = "); scanf_s("%d", &ai);
printf("c = "); scanf_s("%d", &ci);
printf("d = "); scanf_s("%d", &di);
printf("f = "); scanf_s("%d", &fi);
printf("e = "); scanf_s("%d", &ei);
a = ai;
c = ci;
d = di;
f = fi;
e = ei;Didn't find what you were looking for?
Ask your questionAsk a Question
731 491 924 answers to any question