Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
How to increase disk space after backup?
Made a bit-by-bit copy of one disk to another using the command
sudo dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/sdb1 bs=4096 conv=noerror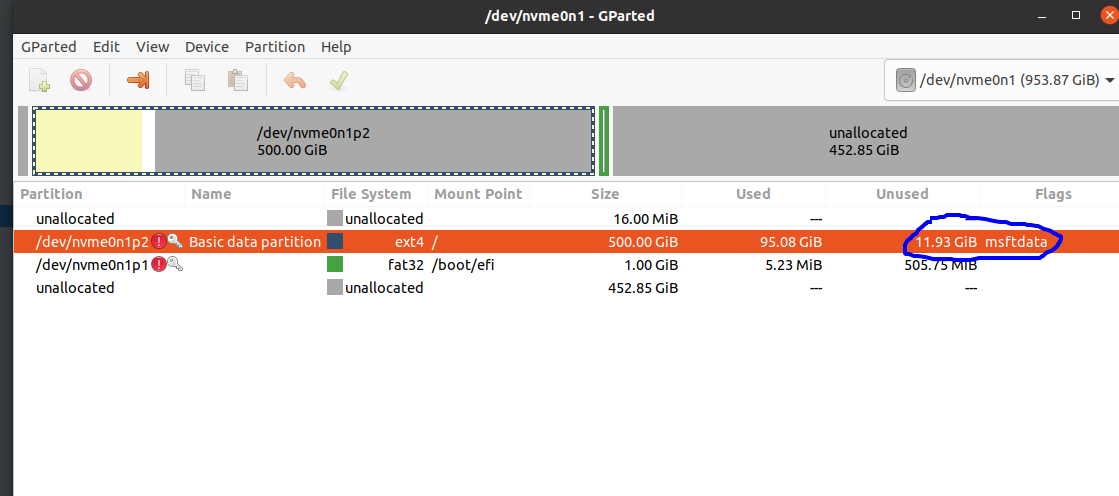
Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
clone disk:
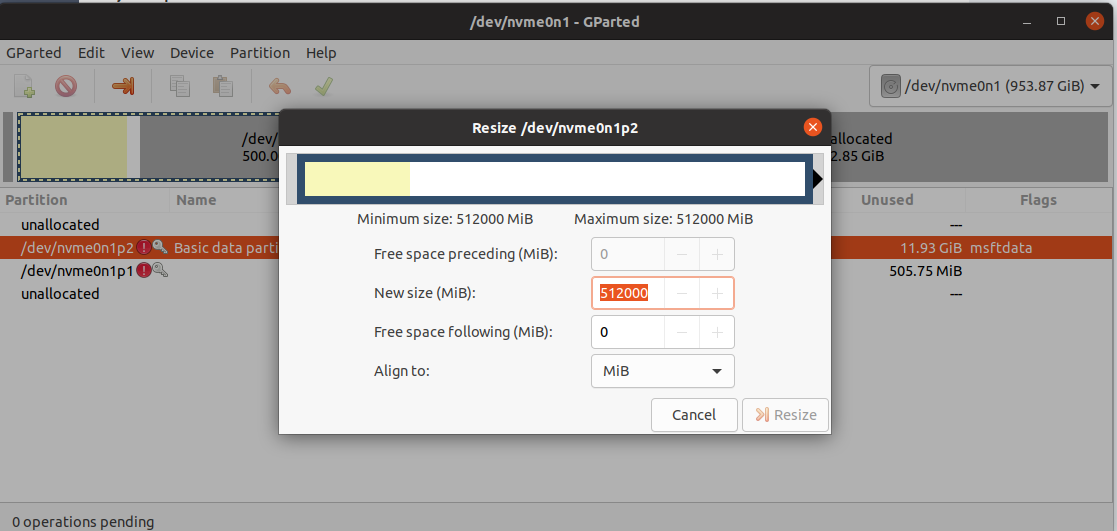
dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/nvme0n1 bs=100M conv=fsync oflag=direct status=progresslsblk /dev/nvme0n1echo ", +" | sudo sfdisk /dev/nvme0n1 -N 2blockdev --rereadpt /dev/nvme0n1e2fsck -f /dev/nvme0n1p2resize2fs /dev/nvme0n1p2e2fsck -f /dev/nvme0n1p2sfdisk --relocate gpt-bak-std /dev/nvme0n1
What's the point of copying a disk to a partition? There was a vinaigrette. We need to decide on the task. If you need a disk image, use some partclone, if you clone, then from disk to disk. Partclone does not save empty space and the image will be smaller.
You can copy byte by byte only to a partition of the same size, and when copying to a partition of a larger size, the total size will remain the same and the extra space will not be automatically used.
There are a lot of utilities, for example, partclone (supports all popular file systems, including ntfs) that can very effectively copy the contents of a partition without affecting its logical objects (files, attributes, access rights, etc.) but at the same time skipping the free area, can copy both to a larger partition and reduce the size if the free space on the source disk allows it (unfortunately, this does not always happen, if the mft area area fails, the reduction limit may not be equal to the occupied disk space, for example, a 500GB partition with 100GB occupied, I could only reduce it to about 200GB, there is no way to fix this, only backup format restore)
There is an excellent utility - clonezilla, regular for most linux, incl. has boot images (based on partclone) which, with simple and clear wizards, allows you to do a lot of useful things with disks.
Didn't find what you were looking for?
Ask your questionAsk a Question
731 491 924 answers to any question