Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
How to explain to a back-end developer why I can't do what he wants?
I have already asked the question. But I repeat once again
There is such a piece of code
'formData.brand'(val) {
let payload = {
names: arr,
values: {
"brand": val
}
}
if (!val) return;
axios.get('../../../json/v1/form/kasko/dependencies', {
params: payload
}).then(response => {
this.$set(this.dependentData, 'brand', {
model: response.data.models,
country: response.data.city
});
}).catch(errors => {
console.error(errors);
});
}valuesI transfer object 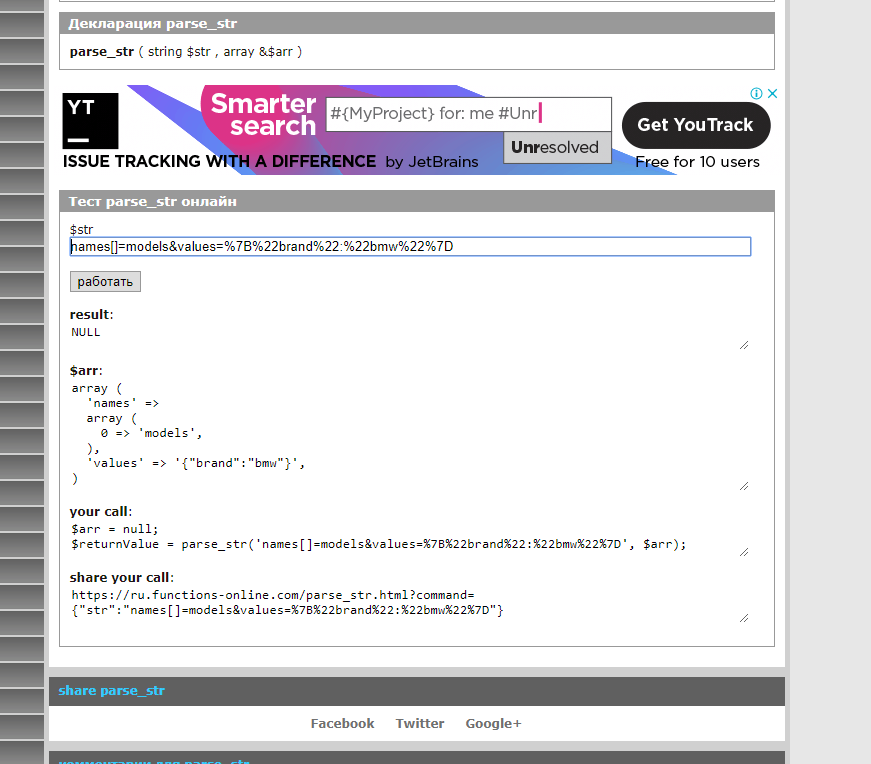
Answer the question
In order to leave comments, you need to log in
Learn query methods. With GET you send a string, to send an object you need to use one of POST, PUT, PATCH and the send object parameter
https://developer.mozilla.org/uk/docs/Web/HTTP/Methods
https://learn.javascript .ru/ajax-xmlhttprequest
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/F...
Your piece of code
axios.get('../../../json/v1/form/kasko/dependencies', {
params: payload
}).then(response => {Performing a POST requestaxios.post('/user', { firstName: 'Fred', lastName: 'Flintstone' }) .then(function (response) { console.log(response); }) .catch(function (error) { console.log(error); });
Teach the backend to write an API contract in https://swagger.io/ then there will be less misunderstanding
You can do whatever the backender wants.
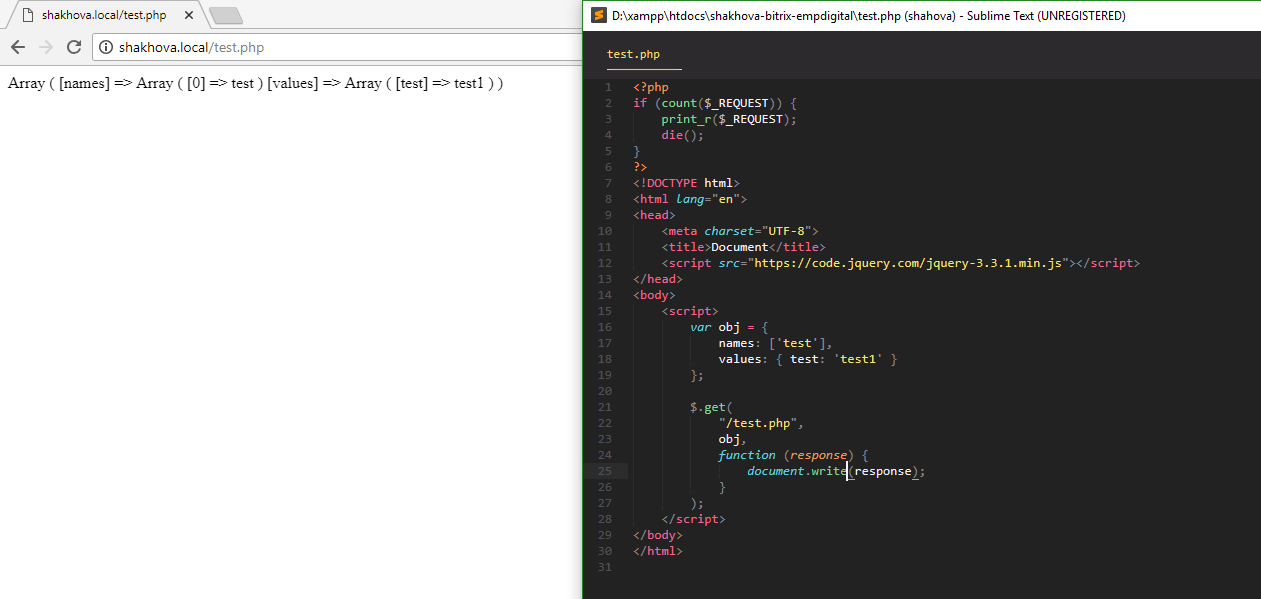
The problem is with Axios. GET parameters, if they contain multidimensional arrays/objects, it converts to json representation, leaving only the top-level linear array. In general, correctly (this was already noted by Vladimir ), GET is for requesting data, and the request parameters usually come in a list.
But still, the protocol allows you to represent arrays, both linear and multidimensional. jQuery does just that, by the way.
In general, to the point. You can use standard Axios features to transform query parameters:
let arr = [1,2,3];
let val = 'BMW';
let payload = {
names : arr,
values: {
brand: val,
},
};
axios.get('http://site.ru?id=1', {
params: payload,
paramsSerializer: function(params) {
let tmp = [];
params.names.forEach(item => {tmp.push(`names[]=${item}`)});
for (let name in params.values) {
if (!params.values.hasOwnProperty(name)) continue;
tmp.push(`values[${name}]=${params.values[name]}`);
}
return tmp.join('&');
},
}).then( ...Array
(
[id] => 1
[names] => Array
(
[0] => 1
[1] => 2
[2] => 3
)
[values] => Array
(
[brand] => BMW
)
)wait, what are you doing? you send to the backend:
- an array of strings where names is a query param and a GET request type, that's ok
- in query param: values which is an object {"brand": "bmw"}, what's that?
you can of course do it like this:
const url = '../../../json/v1/form/kasko/dependencies?values='
const values = {
"brand": val
}
axios.get(url + JSON.stringify(values))
.then(response => {....})
.catch(...);data = {
"names": [{
"models": [{"brand" "bmw"}]
}]
}Didn't find what you were looking for?
Ask your questionAsk a Question
731 491 924 answers to any question